Microsampling
Microsampling offers tremendous practical and ethical advantages over traditional sampling in drug discovery and development. For preclinical studies, microsampling offers advantages of reduced animal usage with less stressful sampling, where serial instead of composite data is possible. For clinical studies, microsampling enables patient centric studies where patients can perform sample collections. This is particularly beneficial for remote sampling where trials can reach participants not accessible in the traditional brick-and-mortar trials. Microsampling accelerates the adoption of decentralized trials (DCT), which play a key role in drug development in the post pandemic environment. Microsampling holds promise for measurements of clinical biomarkers.
Albeit the promise of microsampling, bioanalytical support of (preclinical or clinical) studies can be challenging. Microsamples can be in either dried or liquid states. Dried samples are collected in dried blood spots (DBS) or volumetric absorptive microsampling (VAMS) devices such as Mitra® and Tasso M20®. Although VAMS devices can collect a fixed volume of blood samples regardless of sample hematocrit (HCT), attention needs to be paid for extraction related issues, often leading to pseudo-instability concern. Additionally, regulatory agencies may require bridging of concentration data between dried samples and plasma samples. On the other hand, liquid sample is an option for microsampling where minute samples are collected and processed. For example, capillary microsampling (CMS) and Tasso-SST® are two approaches.
Overall, microsampling offers significant advantages for both preclinical and clinical trials. Nevertheless, extra attention is required to support bioanalysis especially for regulated studies.
Please ask how we can help you navigate bioanalytical challenges for preclinical and clinical studies involving microsampling!

Disclaimer: For illustration purpose, some pictures were taken directly from vendors' websites, i.e., neoteryx.com, tassoinc.com, drawbridgehealth.com, yourbiohealth.com, and weavrhealth.com. For product information, please visit the respective websites. If picture(s) of certain product(s) can't be shown, please contact us to remove it.
References for Bioanalytical Support of Microsampling - Preclinical and Clinical Samples/Studies
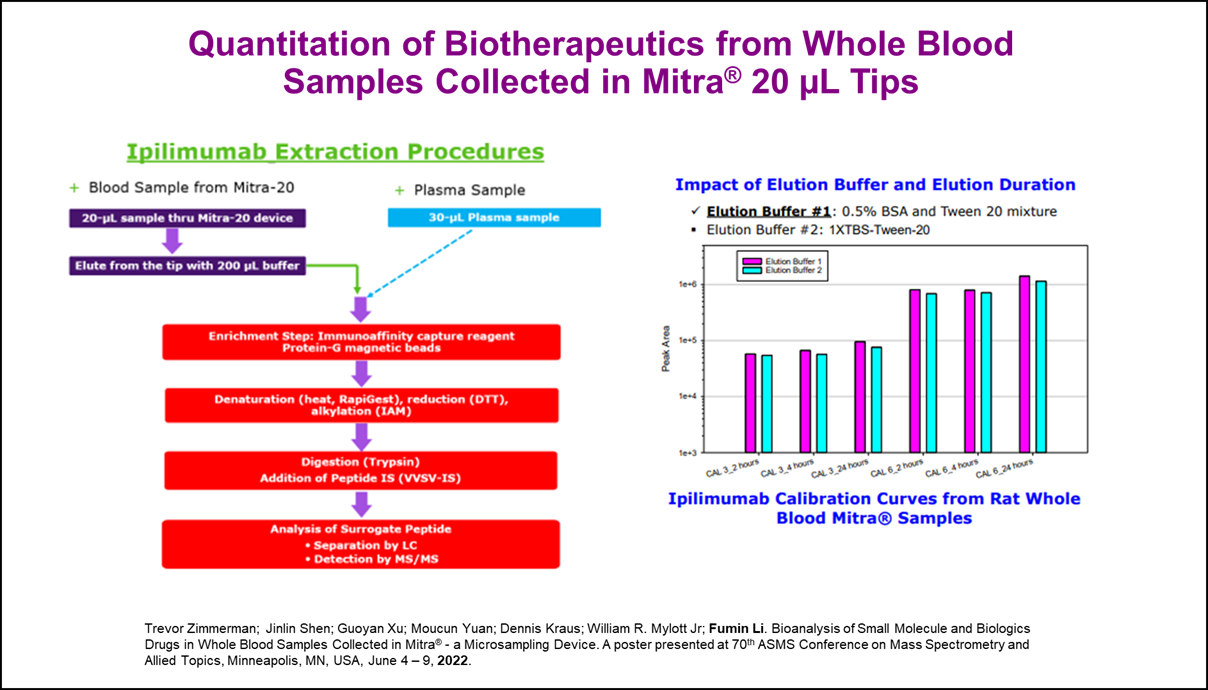
- Trevor Zimmerman; Jinlin Shen; Guoyan Xu; Moucun Yuan; Dennis Kraus; William R. Mylott Jr; Fumin Li. Bioanalysis of Small Molecule and Biologics Drugs in Whole Blood Samples Collected in Mitra® - a Microsampling Device. A poster presented at 70th ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, Minneapolis, MN, USA, June 4 - 9, 2022.
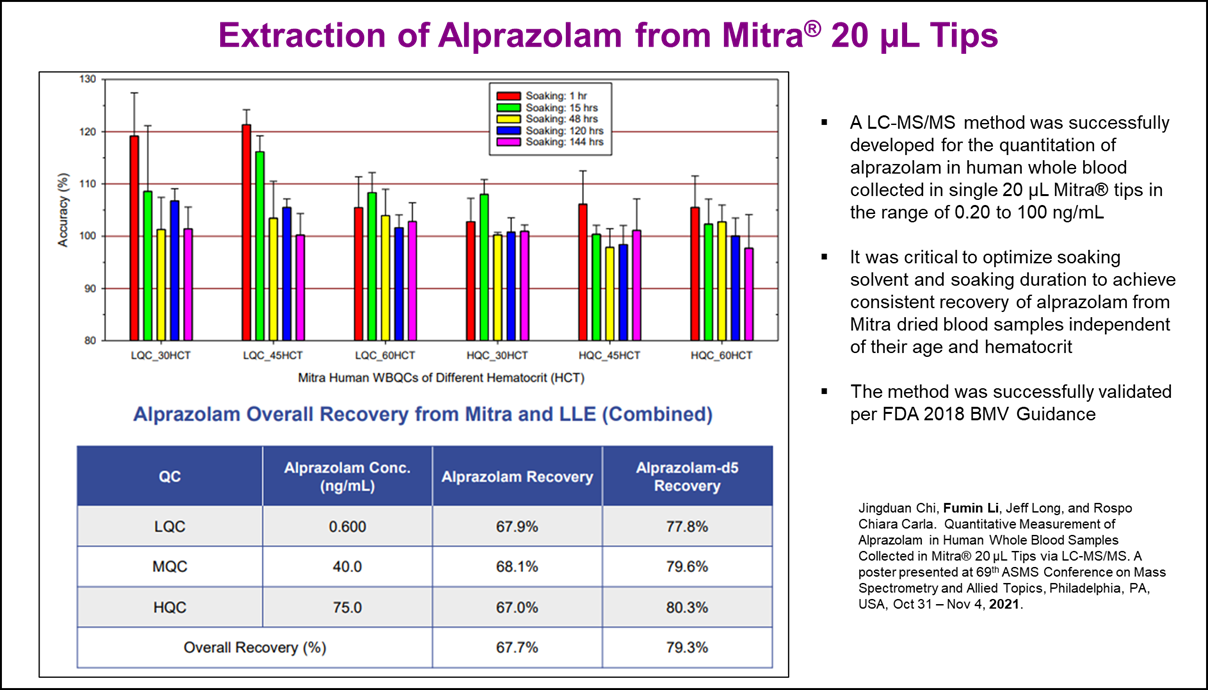
- Jingduan Chi, Fumin Li, Jeff Long, and Rospo Chiara Carla. Quantitative Measurement of Alprazolam in Human Whole Blood Samples Collected in Mitra® 20 µL Tips via LC-MS/MS. A poster presented at 69th ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, Oct 31 - Nov 4, 2021.
- Li F*, Fast DM, Ploch SA. Accurate weighing and dilution-assisted plasma microsampling (AWADA-PM): an easy-to-implement and rugged strategy. Bioanalysis, 2014, 6, 805-817.
- Li F*, Ewles M, Pelzer M, Brus T, Ledvina A, Gray N, Koupaei-Abyazani M, Blackburn M. Case Studies: The Impact of Non-Analyte Components on LC-MS/MS Based Bioanalysis - Strategies for Identifying and Overcoming Matrix Effects. Bioanalysis, 2013, 5, 2409-2441.
- Dried blood spots: the future. Jack Henion, Regina V Oliveira, Fumin Li, Timothy P Foley, and Robert J Pomponio. In: Microsampling in Pharmaceutical Bioanalysis. Unitec House, 2 Albert Place, London N3 1QB, UK (Future Science Ltd) 2013. Pages 48-66 (eBook ISBN: 978-1-909453-58-6). Book Chapter.
- Li F*, Ploch S. Will 'green' aspects of dried blood spot sampling accelerate its implementation and acceptance in the pharmaceutical industry? Bioanalysis, 2012, 4, 1259-1261.
- Li F*, Fast D, Michael S, Stephen, P. Perforated dried blood spot accurate microsampling: the concept and its applications in toxicokinetic sample collection. Featured cover article in J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 655-667.
- Li F*, Fast D, Michael S. Absolute Quantitation of Protein Therapeutics in Biological Matrices by Enzymatic Digestion and Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Bioanalysis, 2011, 3:2459-2480.
- Li F.*, Carrie M, Li F-X, Zulkoski J. LC-MS/MS Sensitivity Enhancement using 2D-SCX/RPLC and its application in the assessment of pharmacokinetics (PK) of clonidine in Dried Blood Spot (DBS).Bioanalysis, 2011, 3:1577-1586.
- Li F*, Zulkoski J, Ding J, Brown W, Addison T. LC-MS/MS Sensitivity Enhancement via Online Sample Dilution and Trapping: Applications in Microdosing and Dried Blood Spot (DBS) Bioanalysis.Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24: 2575-2583.